 RITVERC JSC
RITVERC JSC10, Kurchatova str., 194223,
St. Petersburg, Russia
Phone: +7 812 297-44-63
Fax: +7 812 297-58-87
Email: info@ritverc.com
Url: www.ritverc.com
You are here

Description
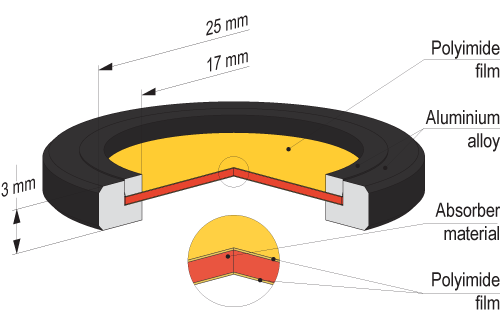
Mössbauer effect reference absorbers contain chemical substances synthesized with either enriched 57Fe (> 95 %) or natural iron. The substances are uniformly dispersed in polyethylene and shaped into discs: 20 mm in diameter, placed between two polyimide films with total thickness of 100 ± 10 μm in aluminium holders. Potassium and potassium-magnesium ferrocyanide [K4Fe(CN)6×3H2O; K2MgFe(CN)6] exhibit unsplit narrow line in Mössbauer absorption spectra. Ferrous oxalate dihydrate [FeC2O4×2H2O] exhibits quadrupole splitting, leading to two narrow lines in Mössbauer absorption spectrum. Metallic iron and iron oxide [αFe; Fe2O3] exhibit magnetic hyperfine splitting, leading to six narrow lines in Mössbauer absorption spectra.
| Description | Thickness, mg 57Fe/cm2 | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Enriched iron reference absorbers | ||
| K2MgFe(CN)6 | 0.25–1.00 | MRA.1.1.X |
| FeC2O4×2H2O | 0.50–1.00 | MRA.1.2.X |
| Fe2O3 | 1.00–2.00 | MRA.1.3.X |
| α–Fe foil | 3 μm | MRA.1.6 |
| Natural iron reference absorbers | ||
| FeC2O4×2H2O | 0.13–0.25 | MRA.2.2.X |
| Fe2O3 | 0.13–0.25 | MRA.2.3.X |
| K4Fe(CN)6×3H2O | 0.13–0.25 | MRA.2.4.X |
| α–Fe foil | 30 μm | MRA.2.6 |
|
* — “X” is the thickness of the reference absorber in mg (57Fe/cm2): |
||
Request: info@ritverc.com

